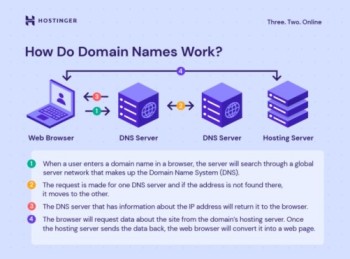
A domain name is a human-readable address used to identify a specific location on the Internet. It serves as the online address for websites,Key Concepts of Domain Names enabling users to access content easily without needing to remember complex numerical IP addresses. A well-chosen domain name can enhance a brand’s online presence and credibility, making it an essential component of establishing a website.
Key Concepts of Domain Names
- Structure of a Domain Name:
- A domain name consists of two main parts: the Second-Level Domain (SLD) and the Top-Level Domain (TLD).
- Second-Level Domain (SLD): This is the main part of the domain name, which often reflects the name of the organization, brand, or purpose of the website (e.g.,
exampleinexample.com). - Top-Level Domain (TLD): This is the suffix of the domain name, indicating the type or origin of the website. Common TLDs include:
- Generic TLDs (gTLDs): Such as
.com,.org,.net,.info, etc. - Country Code TLDs (ccTLDs): Such as
.uk(United Kingdom),.in(India),.ca(Canada), etc. - New gTLDs: A wide range of new domain extensions like
.tech,.shop,.blog, etc.
- Second-Level Domain (SLD): This is the main part of the domain name, which often reflects the name of the organization, brand, or purpose of the website (e.g.,
- Domain Registration:
- Domain names must be registered through accredited registrars, such as GoDaddy, Namecheap, or Google Domains. Registration usually involves:
- Choosing a domain name that is available and not already registered by someone else.
- Providing contact information and paying a registration fee, typically on an annual basis.
- Renewing the domain periodically to maintain ownership.
- Domain Name System (DNS):
- The DNS is a hierarchical system that translates domain names into IP addresses, allowing browsers to locate and connect to the corresponding web servers. The DNS functions like a phonebook for the Internet, mapping user-friendly names to numeric IP addresses.
- Domain Name Characteristics:
- Memorability: A good domain name should be easy to remember, spell, and pronounce, helping users recall the site.
- Length: Shorter domain names are often more effective, as they are easier to type and remember. Ideally, keep it under 15 characters.
- Keywords: Incorporating relevant keywords related to the business or website can improve search engine optimization (SEO) and make the domain more descriptive.
- Brandability: The domain name should reflect the brand or identity of the organization, conveying its values and purpose.
Types of Domain Names
- Personal Domain Names
- Used by individuals for personal branding, blogs, portfolios, or resumes. For example,
yourname.com.
- Business Domain Names
- These represent companies, organizations, or brands and are typically used for their official websites. For example,
yourbusiness.com.
- E-commerce Domain Names:
- Domain names specifically designed for online stores, often including keywords related to the products sold. For example,
bestonlinestore.com.
- Non-Profit Domain Names
- Used by non-profit organizations, often utilizing the
.orgTLD. For example,charityname.org.
- Geographic Domain Names:
Choosing a Domain Name
When selecting a domain name, consider the following tips:
- Brainstorm Ideas
- Generate a list of potential domain names that reflect your brand or the purpose of your website.
- Check Availability:
- Use domain registration sites to check the availability of your desired domain names.
- Avoid Hyphens and Numbers:
- Choose the Right TLD:
- While
.comis the most recognized TLD, choose one that suits your website’s purpose (e.g.,.orgfor non-profits,.shopfor e-commerce).
- Consider Future Growth:
- Select a domain name that can accommodate potential growth or changes in your brand or business.
Domain Name Management
- DNS Management
- After registering a domain, you may need to configure DNS settings to link it to your web hosting provider. This includes setting up A records, CNAME records, and MX records for email services.
- Domain Privacy Protection:
- Many registrars offer privacy protection to keep personal information (like name, address, and email) confidential, preventing it from being publicly accessible in the WHOIS database.
- Domain Renewal:
- Domains need to be renewed periodically (usually annually). Set reminders to avoid losing your domain name, as failure to renew can lead to it becoming available for others to register.
- Transfer Domain Names
- If you decide to switch registrars or hosting providers, you can transfer your domain name. The process involves unlocking the domain, obtaining an authorization code, and following the new registrar’s transfer process.
Conclusion
A domain name is a vital aspect of any online presence, acting as the primary address for users to access websites. Selecting the right domain name involves careful consideration of its relevance, memorability, and suitability for your brand or organization. Understanding how to register, manage, and utilize a domain name effectively will significantly impact your success in the digital landscape. If you have questions or need further assistance regarding domain names, feel free to ask!