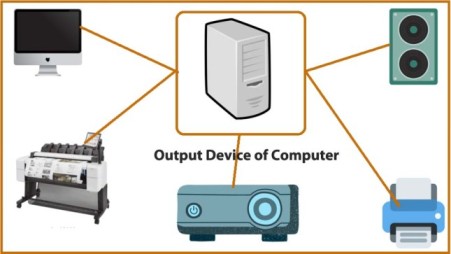
Output Devices
Output devices are essential components of a computer system that convert processed data from the computer into a form understandable by users. They play a critical role in presenting information, whether visually, audibly, or through other means. Understanding output devices is fundamental for anyone interested in technology, computing, and information systems. This article explores the various types of output devices, their functions, and their significance.
What are Output Devices?
Output devices are hardware components that receive data from a computer’s processing unit and translate that data into a human-readable format. They allow users to receive results from computations, visual presentations, or audio feedback, facilitating effective communication between the computer and the user.
Types of Output Devices
Output devices can be categorized into several types based on their functionality and the type of output they provide:
1. Monitor
- Description: A monitor is a visual display device that presents images, text, and videos from the computer.
- Functionality:
- It receives data from the computer’s graphics card and displays it on a screen.
- Monitors come in various technologies, including LCD, LED, and OLED.
- Types of Monitors:
- Flat-panel Monitors: Thin and lightweight, suitable for modern workspaces.
- Curved Monitors: Designed to provide an immersive viewing experience.
2. Printer
- Description: A printer is an output device that produces hard copies of documents and images on paper.
- Functionality:
- It translates digital data into printed form, using ink or toner to create text and graphics.
- Types of Printers:
- Inkjet Printers: Use liquid ink to produce high-quality prints, suitable for photos and graphics.
- Laser Printers: Use toner and heat to produce faster, high-quality text documents.
- Dot Matrix Printers: Use a series of pins to create characters on paper; often used for multi-part forms.
3. Speakers
- Description: Speakers are audio output devices that convert digital audio signals into sound.
- Functionality:
- They allow users to hear music, alerts, notifications, and other audio from the computer.
- Types of Speakers:
- Built-in Speakers: Integrated into laptops and monitors for convenience.
- External Speakers: Standalone units connected via Bluetooth or audio cables for improved sound quality.
4. Headphones
- Description: Headphones are a personal audio output device worn on or over the ears.
- Functionality:
- They provide a private listening experience, ideal for music, gaming, or video conferencing.
- Types of Headphones:
- Wired Headphones: Connected to the computer with a cable.
- Wireless Headphones: Use Bluetooth technology for a cord-free experience.
5. Projector
- Description: A projector is an output device that displays images and videos onto a large screen or wall.
- Functionality:
- It projects the visual output from a computer or video source, making it ideal for presentations and large group viewing.
- Types of Projectors:
- DLP Projectors: Use Digital Light Processing technology for high-quality images.
- LCD Projectors: Utilize Liquid Crystal Display technology for vibrant colors.
6. Plotter
- Description: A plotter is an output device used for printing large-scale graphics and designs, typically in engineering and architecture.
- Functionality:
- It produces high-quality vector graphics, such as blueprints and maps, using pens or ink.
- Types of Plotters:
- Inkjet Plotters: Use ink cartridges to create color graphics.
- Laser Plotters: Use laser technology for precision and speed.
7. Haptic Devices
- Description: Haptic devices provide tactile feedback to users, simulating the sense of touch.
- Functionality:
- They allow users to experience sensations through vibrations or force feedback, commonly used in gaming and virtual reality.
- Applications:
- Enhance user interaction in simulations, training programs, and gaming environments.
8. Braille Display
- Description: A Braille display is an output device designed for visually impaired users, converting text into Braille.
- Functionality:
- It uses a series of small pins that raise and lower to create Braille characters, allowing users to read text outputs.
- Applications:
- Used in conjunction with computers and mobile devices to provide access to digital information.
Importance of Output Devices
Output devices are crucial for several reasons:
- Information Presentation: They enable users to receive processed data in a comprehensible format, allowing for effective decision-making and understanding.
- User Interaction: Output devices enhance the overall user experience by providing audio and visual feedback, facilitating better interaction with the computer.
- Documentation: Printers and plotters allow for the creation of physical copies of documents, which are essential for record-keeping, sharing, and presentation.
- Accessibility: Specialized output devices, such as Braille displays and haptic devices, ensure that technology is accessible to individuals with disabilities.
- Entertainment: Speakers, monitors, and projectors enhance entertainment experiences, allowing users to enjoy movies, music, and games with high-quality output.
Conclusion
Output devices are integral components of computer systems, enabling users to receive and interact with information generated by the computer. From monitors and printers to speakers and Braille displays, each output device serves a unique purpose in facilitating communication between the user and the machine. Understanding the various types of output devices and their functions is essential for anyone involved in technology and computing.